South central Oregon is pioneering a strategy for bolstering forest resilience to wildfire and climate
change.
How? In the short term, land managers will reduce the shrubs, dead wood and other fuels that feed severe
reburns. They will also accelerate forest recovery by establishing disease-
and drought-resilient seedlings.
Once the forest is stable, they will control fuel levels through widespread application of low-intensity
fire.
Image: Jade Elhardt.
A team of experts conducted a highly detailed geospatial analysis of
the massive fire footprints.
By analyzing fuel loads, seed sources,
burn contiguity, vegetation type and forest mortality, the
team estimated the scale of need for different restoration treatments.
Inset image: Steve Rondeau / Klamath Tribes Natural Resources Department. Map: Julia Twichell / American Forests.

The team pinpointed areas where replanting and fuel control can facilitate recovery.
In areas with extensive forest loss, trees can regrow naturally only
where seeds from surviving trees can disperse. By identifying areas located too far from seed sources, the team determined where planting seedlings can expedite reforestation.
Meanwhile, assessment of shrubs, dead wood and other fuels indicated where fuel control tactics could minimize the risk of
severe reburns.
Inset image: Libby Pansing / American Forests. Map: Julia Twichell / American Forests.

The result? A full breakdown that estimates the scale and cost of activities needed to treat and restore all
sections of the fire footprint.
 250,000 acres
250,000 acres
reforestation
(natural
and planted)
 92,000 acres
92,000 acres
meadow
restoration and
fuel reduction
 203,000 acres
203,000 acres
fuel treatment
without
reforestation
 33,000 acres
33,000 acres
prescribed fire
and other
maintenance
hover to see more
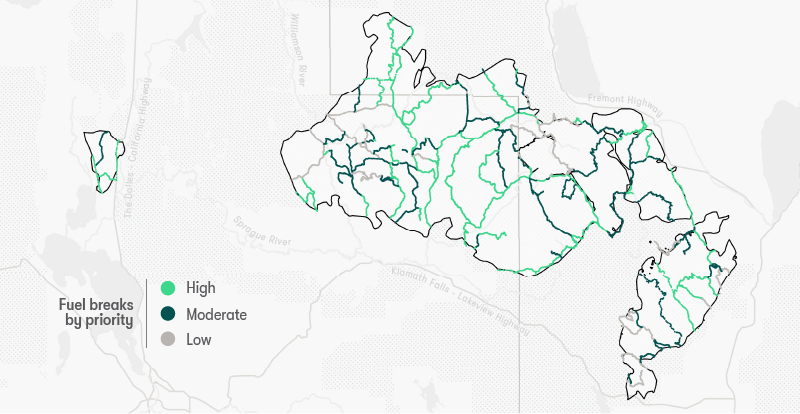
The team also mapped 586 miles of fuel breaks, proposing a network of
corridors for firefighters that would also facilitate use of prescribed fire.
Maintaining cleared corridors provides
access routes for firefighters and facilitates the safe use of
prescribed fire. This proposed network of fuel breaks aligns
with roads and areas already cleared by fire.
Background image: Fremont-Winema National Forest / Flickr. Inset map: Julia Twichell / American Forests.